Has it ever occurred to you that your cooking oil got reduced after frying something? What happened here? Did oil evaporate?
But when we heat oil, we don’t see any misty smoke coming out of it like water.
So this naturally bears the question, does oil evaporate too?
The answer is, some of the particles of oil evaporate and some don’t. When we heat something there are two factors to consider- the smoke point and the boiling point. The boiling point is greater than the smoke point for vegetable oils or cooking oils. As a result, oil decomposes and some types of molecules evaporate.
Still not enough to quench your thirst? Let’s dig into the details as we go!
Can Oil Evaporate?
Some of the oils can evaporate and some can’t. How does that even happen, right? Let’s get into the details!
Let’s first understand evaporation correctly. We don’t wanna sound like your high school chemistry teacher so we’ll keep it simple. But if you’re still interested in chemistry, you can check out how intermolecular and intramolecular forces work.
Evaporation is related to boiling point and smoke point. At the boiling point, the substance evaporates as a whole molecule. But at the smoke point, it decomposes into various molecules first. Then some of the molecules evaporate and some don’t. That’s all the chemistry you have to know.
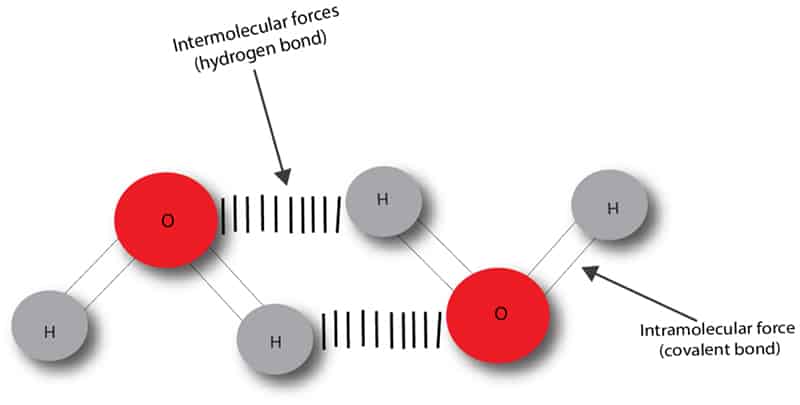
Let’s take water as an example. When we heat water at 100°C, heat alone can’t break apart the intramolecular bond. But the intermolecular bond is broken at this temperature and the water starts to vaporize.
Now let’s get back to oil evaporation. The issue of oil evaporating can be as confusing as caffeine being cooked out.
Let’s start with knowing the types of oil. There are two different types of oils we can get from mother nature. They are volatile oil and fixed oil.
Volatile oils are the ones we get from the roots, barks, or petals of trees. They are usually used for aromatic purposes in different perfumes.
On the other hand, fixed oils are the ones we get from the seeds, kernels, or nuts. They are our regular cooking oils. They’re also known as vegetable oils. Later they are refined, bleached, flavored for commercialization.
Volatile oils are the oils that evaporate. Because when heated, they reach their boiling point before the smoke point.
On the other hand, vegetable oils like olive, coconut, soybean, etc oils reach their smoke point first. This leaves no boiling point for cooking oils.
We can’t determine at what temperature vegetable oils evaporate. Because they don’t remain the same oil as they were before heating. Also, the liquid base of the oil stays as it is even when it is heated continuously.
Now you might be wondering, are all the vegetable oils the same? Well no, there are different types of vegetable oils. For example olive oil, palm oil, soybean oil, canola oil, sunflower oil, etc.
All these have different molecules but they work the same. We’ll know more about this as we move forward.
Does Cooking Oil Really Evaporate?
Oftentimes, we can confuse oil smoking or burning as evaporation. Even when we see the oil level decreasing in our bottle, we blame evaporation.
But is that really what’s happening? Let’s find out!
Does Oil Evaporate at Room Temperature?
If we leave cooking oil open at room temperature, its smell wears off after some time. What happens here? Does oil evaporate if left open?
Technically, yes. This is evaporation. But this is not the evaporation of the oil molecule. Only the molecules that contain scent get evaporated here. That’s why we can’t smell it.

We’ve learned before that oil is made of several different types of substances. Each of these substances vaporizes under different circumstances. When we open the cap of the oil container, we can smell the oil. It means the scent is vaporizing.
Does Oil Evaporate When Heated?
When vegetable oil is heated to a certain temperature, we can see smoke coming out of the pan. You still might be wondering, “if oil does not evaporate, what is this smoke then?”
Well, do you remember that vegetable oils consist of several different ingredients? When the temperature reaches the smoke point, the oil is destroyed. It breaks into several separate substances.
These substances as well as the base oil are burnt continuously through heating. As a result, carbon dioxide and other gases are emitted which we see as smoke.

Due to this burning, the smoke and other particles start flying around. This gets vented out through your kitchen vent. You’ll notice that after a certain period of time, your vent gets greasy and sticky. This smoke and broken oil particles have a crucial role in this crime.
Now you can heat oils in different ways. You can heat them in your oven, you can bake with vegetable oil. Or maybe you just wanna heat the oil on your stove. Either way, the scenario about the breakdown of oils is exactly the same.
It’s time for another big question. And that is, “Does oil reach its smoke point when I’m frying something in it?”
The answer is, no. The oil doesn’t shoot for its smoke point if you start frying something. The oil doesn’t keep consuming the heat alone when something’s being fried in it.
Rather the oil conveys the heat to the food and cooks it. This is why the amount of oil gets lessened when you fry something.
We’ve mentioned earlier that each type of vegetable oil has its own smoke point. There are also different uses for different cooking oils. So here’s a list of the most common vegetable oils and their approximate smoke points-
| Oil | Smoke Point | |
| Canola Oil | 205°C | 401°F |
| Mustard Oil | 250°C | 480°F |
| Butter | 150°C | 302°F |
| Castor Oil | 200°C | 392°F |
| Corn Oil | 23F°C | 450°F |
| Soybean Oil | 234°C | 453°F |
| Olive Oil | 207°C | 405°F |
| Almond Oil | 221°C | 430°F |
If you don’t want your oil to be burnt, you should know the temperature of the oil before frying. Because, if the oil hits the smoke point, the nutrition facts of the oil will be compromised. It will affect the taste of the food too.
But you can’t check the temperature with your bare hands, can you? You can get a thermometer that will read the temperature of the oil.
Of course, not all thermometers show pinpoint temperature. So you might get confused about which would be the best choice. To ease your pain, here are our favorite picks from the market-
Kizen Digital Meat Thermometers for Cooking

ThermoPro TP19H Waterproof Digital Meat Thermometer

Now you have an excellent thermometer to read the temperature. It’s recommended to start frying 50-60°F before the temperature heats the smoke point.
If you start frying after the oil reaches its smoke point, your food will be burnt on the outside. But it’ll still be raw inside. This could be the worst-case scenario ever!
What Happens after Heating Oil?
Now you might wanna ask, “what happens if I keep my food in the oil and it cools down?”
Well, you don’t wanna do that. If you leave your food in before heating it properly, your food might get soggy. The same thing happens if you start frying before the required temperature.
Our target is to keep the food in the oil for as little as possible without burning or undercooking it. The longer they stay in the oil, the more oil they will suck in.
As a result, you’ll find your food totally soggy and oily. If you thought that the oil was reduced because of evaporation, it didn’t. The oil was simply consumed by the food you’re frying.
Can You Reuse Frying Oil?
Yes, you can definitely reuse frying oil. After you’ve used the oil once, all you have to do is let it cool down, skim the oil and store. After that, you can use it again.

But you can’t store used oils for a long time. They can expire just like cooking spray after a certain period of time. You should get rid of used oils after 4-5 weeks of storing.
Hold on, we’re not done yet! You sure can reuse oil if you want. But how safe is reusing frying oil?
Reusing frying oil is not safe at all! Do you know canola, soybean, corn oil, etc. form a toxin named 4-hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal when reheated? It is also known as HNE in short.
Consuming HNE can increase the risk of different heart diseases, liver disorders, and even cancer!
On top of that, reheating oil increases cholesterol. Too much cholesterol also leads to various heart diseases.
So it is better to avoid reusing cooking oil for health benefits. But you should definitely get rid of the oil if it was burnt at the time of first use.
That was pretty much all the information about oil evaporation. Hope you’re clear on whether or not your oil is evaporating away.
FAQs
Question: Does oil dry up?
Answer: No, oils don’t dry up. But if left open in the open air for too long, oils might react with the oxygen in the air. This will add several oxidation products to the oil which will lead the oil to get thickened.
Question: How long does it take for volatile oils to evaporate?
Answer: It depends on which volatile oil we’re talking about and how consistent the oil is. At room temperature, some oils take weeks and some can take months or even years.
Question: Does oil evaporate in a car?
Answer: The oils used in vehicles are always ready to be evaporated at high temperatures. Because they are volatile oils. The higher the volatility, the higher it tends to evaporate.
Question: Do vegetable oils freeze?
Answer: yes, some vegetable oils can freeze. Different vegetable oils freeze at different temperatures. For example, you can freeze corn oil at -11°C.
Bottom Line
We hope you’ve got your answer of does oil evaporate or not. Remember one thing, try to avoid oily foods as much as possible. It will enable you to live a healthier life.
But it doesn’t hurt giving in to some delicious chicken or french fries once in a while! So, happy frying and enjoy your meal!
- How Long Does Vegan Butter Last? Mystery Solved - January 9, 2024
- How Long Does Vegan Mayo Last - January 2, 2024
- From Pot to Plate: How Long Does Vegan Chili Last in The Fridge? - December 26, 2023





 How to Make Rice A Roni Not Mushy? [Instant Fix & Prevention]
How to Make Rice A Roni Not Mushy? [Instant Fix & Prevention]